To protect the legitimate rights of patent holders, China introduced a patent term compensation system in the fourth amendment of the Patent Law. According to Article 42, Paragraph 2 of the Patent Law, if an invention patent is granted more than four years after the filing date and more than three years after the request for substantive examination, the State Council’s patent administration department, upon the patent holder’s request, should provide a term adjustment to compensate for unreasonable delays during the patent authorization process. Additionally, per Article 42, Paragraph 3, a pharmaceutical patent term compensation system was established to promote pharmaceutical research and development, improve public health, and compensate for time lost during the approval process for new pharmaceuticals.
How to Apply for Patent Term Compensation
Only invention patents are eligible for patent term compensation, and the request must be made within three months of the patent grant announcement. A fee of 200 RMB must be paid. The three-month deadline is non-extendable and non-restorable.
Once the request is submitted, CNIPA will examine the case and notify the patent holder of the additional number of days granted. If the extension exceeds one year, the patent holder must pay the annual fee for the increased period. The updated patent registration information, along with the term compensation details, will be announced in the Patent Register.
How to Calculate the Days of Patent Term Compensation
There are no specific limitations for invention patents, but for pharmaceutical patents, the maximum compensation term is five years, and the total term of validity cannot exceed 14 years from the date of approval for sale.
1. For invention patents, the calculation formula for the compensation term is as follows:
Patent Compensation term = (D1 - D2) - T1 - T2
o D1 refers to the date of the announcement of the grant.
o D2 refers to the date on which either four years have elapsed since the filing date of the invention patent application or three years have elapsed since the request for substantive examination, whichever is later. For PCT national phase applications, the filing date refers to the date of entry into the national phase in China, rather than the international filing date.
o T1 refers to any reasonable delay during the examination process.
o T2 refers to delays caused by the applicant, such as requests for extensions or deferred examination.
2. For pharmaceutical patents, the calculation formula for the compensation term is as follows:
Pharmaceutical Patent Compensation term = D3 - D4 -5
The total validity term is calculated as follows:
Total Validity Term = (D5 - D3) + Compensation term + Pharmaceutical Patent Compensation term
o D3 refers to the date of approval for sale.
o D4 refers to the filing date of the patent.
o D5 refers to the 20-year expiration date of the patent.
Recent Examples of Patent Term Compensation
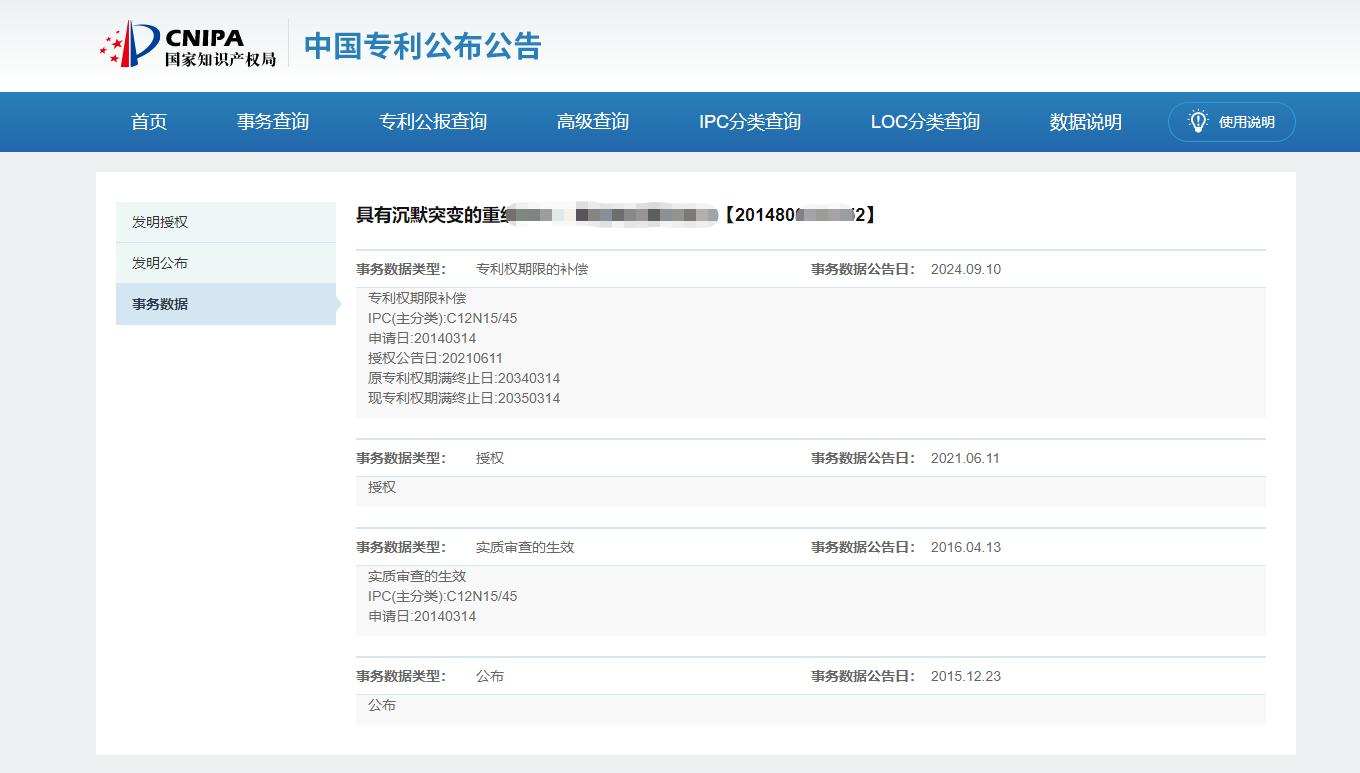
Since the first publication of patent term compensation on August 27, 2024, more than 500 patents have been granted term extensions. In a recent example, the national phase application of PCT/US2014/027447, filed in 2014 and granted on June 11, 2021, met the criteria for adjustment according to Article 42. A 365-day extension of validity was granted, as the request for substantive examination had been made in 2015.
In conclusion, China's patent term compensation system plays a critical role in safeguarding the interests of patent holders, particularly in addressing delays in the authorization process for invention and pharmaceutical patents. This system not only strengthens patent protection but also encourages innovation and development, especially in the pharmaceutical sector. By compensating for lost time due to administrative or approval delays, the system provides a more balanced and fairer framework for inventors and pharmaceutical developers, fostering a healthier environment for technological advancement and public welfare.

