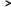Recently, Chongqing No. 5 Intermediate People's Court made first instance judgment toward the Chongqing Pigeon Electric Wire & Cable Co., Ltd. sued Chongqing Gehuang Electric Wire & Cable Group Co., Ltd. trademark infringement and unfair competition dispute case.
The verdict showed that Gehuang should publish a statement in the newspaper to eliminate the impact of infringing on the exclusive rights of the Pigeon series of trademarks and the unfair competition that infringes on the name rights of Pigeon’s business. Gehuang shall immediately stop the infringement actions involved in the case, and compensate for economic losses and the reasonable expands paid by Pigeon to stop the infringement behavior ten million yuan in total.
The two trademarks are both oval-shaped structures, distributed on both sides of the oval, one is "Pigeon", and the other is "GEHUANG"; above the oval are the images of pigeons spreading their wings, but there are certain differences in movement and size. The Pigeon brand is a mountain with three peaks in the oval, with the English word ‘PIGEON’, while ‘Ge Huang’ is three rings with Pinyin ‘GEHUANG’.
In December 1980, Pigeon Company applied for the "Pigeon and the graph" trademark, which was registered on April 15, 1981, and was approved for use in Category nine "electric wire" commodities.
Pigeon series of trademarks has accumulated relatively high popularity and brand awareness through the Pigeon Company’s continual operation. Since 2002, "Pigeon brand ‘PIGEON’ and the graph" trademark has been recognized as a "Chongqing Well-known Trademark" for many times; and it was recognized as a well-known trademark on January 15th 2010.
In March 2005, the legal representative of Gehuang Company applied for the combined trademark of "‘GEHUANG’ and graphics" on Category nine "electric wires; cables" and other commodities, and was registered in December 2007. In April 2013, the former Trademark Review and Adjudication Board ruled that the Gehuang trademark infringed the trademark rights of the "Pigeon" series of trademarks and the right of enterprise name, and the Gehuang trademark has been revoked. Regarding the ruling, the legal representative of Guhuang Company expressed dissatisfaction, and spent five years, through continuous appeals, went through all the administrative proceedings in trademark disputes in an attempt to restore the Gehuang trademark.
In May 2018, Beijing Higher People's Court made a final judgment, rejected the appeal of Gehuang Company, upheld the original judgment, established the fact that the ‘Gehuang’ trademark was invalid, and announced that Pigeon Company declared that Gehuang trademark invalid through administrative litigation and other means.
The trademark dispute initially ended here, but after the Gehuang Company lost the lawsuit, the Gehuang Company still used the invalidated trademark.
In September 2018, the Pigeon Company sued Gehuang Company and the Happy Time Building Materials Business Department of the Emerging Industry Development Zone in the Fifth Intermediate People's Court of Chongqing City (it is a distributor of "Gehuang" products, and has an associated relationship with Gehuang Company), and required it to bear civil liability for trademark infringement and unfair competition. In this civil lawsuit, Pigeon bears the relevant liabilities for the serious impact caused by the trademark infringement and unfair competition of Gehuang, and the losses caused to Pigeon.
This time, Pigeon won the case comprehensively.
In this litigation, Chongqing No.5 Intermediate People’s Court considered that as for the whole case, the defendant Gehuang Group Co. Ltd. imitated the plaintiff from the company name and trademark, the time length of infringement has lasted for more than ten years, and the infringing products covered many types of models of electric wire and cable products. There has been a punishment history due to the counterfeiting of the plaintiff’s products. In this way, the maliciousness of infringement is obvious, and the circumstances are serious.